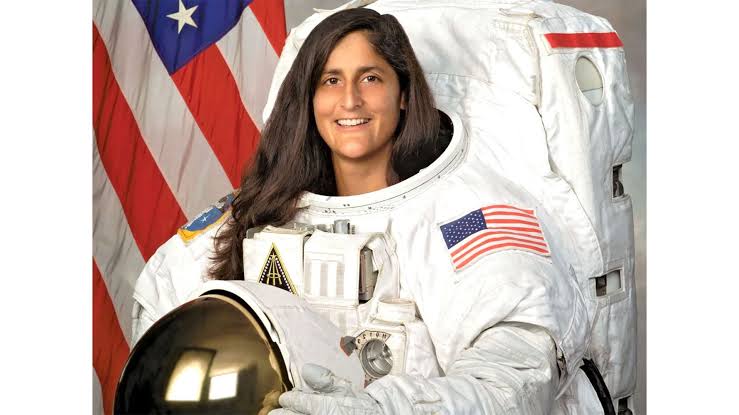
Astronaut Sunita Williams, renowned for her extraordinary space missions, has been under intense health monitoring by NASA after experiencing significant weight loss during her extended stay aboard the International Space Station (ISS). While weight fluctuations are common due to the unique conditions of space travel, the scale of Williams’ weight loss raised concerns and prompted close monitoring by NASA’s medical team.
The Impact of Microgravity on Astronauts
Microgravity, or the near-weightless condition experienced in space, has several physiological effects on the human body. Astronauts often face muscle atrophy, bone density loss, and fluid redistribution. Weight loss is another common issue, as the body adapts to this altered environment. NASA has long been aware of these challenges, and astronauts like Williams undergo extensive health monitoring to mitigate these effects. For more on how microgravity impacts the human body, read more here.
Sunita Williams’ Extended Stay
Williams, known for holding the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman, spent an extended period aboard the ISS. Her mission, which involved working on scientific experiments, conducting spacewalks, and assisting in the space station’s upgrades, stretched over months. Despite the highly demanding nature of her work, Williams experienced a noticeable drop in weight during her mission, prompting NASA to conduct additional health assessments.
NASA’s Response
NASA has a comprehensive health monitoring program to safeguard astronaut well-being during their space missions. This includes regular health checkups that assess aspects like bone density, muscle mass, and metabolic function. NASA also customizes diets and exercise routines to counteract the physical strain caused by space conditions. During her mission, Williams was likely provided with a tailored nutrition plan to help maintain her weight and overall health. For more on NASA’s approach to astronaut health, you can read further here.
The Importance of Health Monitoring
The health of astronauts is crucial not just for their own well-being but also for the success of long-term space missions. As NASA looks ahead to missions to Mars and beyond, it is vital to understand how prolonged space travel affects human health. Cases like Williams’ provide valuable insights into how astronauts’ bodies react to extended exposure to space conditions. These findings will be integral to ensuring the success of future missions beyond Earth’s orbit.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring
NASA uses cutting-edge technology to monitor astronauts’ health in real-time. Wearable devices track various health metrics, including heart rate, oxygen levels, and muscle strength, helping to ensure astronauts stay healthy while in space. Continuous monitoring allows NASA to make adjustments to exercise regimens or diet plans to keep astronauts in optimal condition. This technology plays a pivotal role in maintaining astronaut performance and health during long missions.
Conclusion
Sunita Williams’ experience highlights the challenges astronauts face when on long-term space missions. NASA’s monitoring efforts help ensure astronauts’ health is maintained during their time in space. With the goal of exploring more distant destinations like Mars, it will be crucial to have a deeper understanding of the effects of space travel on the human body. Williams’ case serves as a significant study in this area, helping shape the future of human space exploration.
Read more on our more trending special page